Religion in India
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about Republic of India's religious demographics. For religions originating in the Indian subcontinent, see Indian religions.
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of India |
|---|
 |
| History |
| People |
| Cuisine |
| Religion |
| Sport |
The western and northern part of India have been the home of one of the most ancient civilization of the world called Indus valley civilization. Most of the shrines, ancient temples of Hinduism and the birthplace of Hindu saints are in India. Allahabad hosts the biggest religious festival Kumbhamela, where Hindus from all over the world come together to take a bathe in the confluence of three sacred rivers of India: Ganges, Yamuna, and Saraswati. It is also home of around 95% world population of Hindus. The Indian diaspora in the West has popularised many aspects of Hindu philosophy such as yoga, meditation, Ayurvedic medicine, divination, karma, and reincarnation.[3] The influence of Indian religions has been significant all over the world. Several organisations, such as the Hare Krishna movement, the Brahma Kumaris, the Ananda Marga, and others have spread Indian spiritual beliefs and practices.
According to the 2011 census, 79.8% of the population of India practice Hinduism and 14.2% adhere to Islam, while the remaining 7.37% adheres to other religions (Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, Jainism and various indigenous ethnically-bound faiths).[1] Zoroastrianism and Judaism also have an ancient history in India, and each has several thousands of Indian adherents. India has the largest population of people adhering to Zoroastrianism (i.e. Parsis and Iranis) and Bahá'í Faith in the world,[4] even though these religions are not native to India. Many other world religions also have a relationship with Indian spirituality, such as the Baha'i faith which recognises Buddha and Krishna as manifestations of the God Almighty.[5]
The Muslim population of India is the third largest in the world. India also has the third largest Shia population in the world and being the cradle of the Ahmadiyya Islam, it is one of very few countries in the world with at least 1 million Ahmadi Muslims. The shrines of some of the most famous saints of Sufism, like Moinuddin Chishti and Nizamuddin Auliya, are found in India, and attract visitors from all over the world.[6] India is also home to some of the most famous monuments of Islamic architecture, such as the Taj Mahal and the Qutb Minar. Civil matters related to the community are dealt with by the Muslim Personal Law,[7] and constitutional amendments in 1985 established its primacy in family matters.[8]
Contents
History
Main article: Indian religions
See also: Religious thinkers of India and Indian philosophy
Pre-historic religion
Evidence attesting to prehistoric religion in the Indian "subcontinent" derives from scattered Mesolithic rock paintings depicting dances and rituals. Neolithic pastoralists inhabiting the Indus Valley buried their dead in a manner suggestive of spiritual practices that incorporated notions of an afterlife.[9] Other South Asian Stone Age sites, such as the Bhimbetka rock shelters in central Madhya Pradesh and the Kupgal petroglyphs of eastern Karnataka, contain rock art portraying religious rites and evidence of possible ritualized music.[10]Indus Valley Civilization
The Harappan people of the Indus Valley Civilisation, which lasted from 3300 to 1400 BCE and was centered on the Indus and Ghaggar-Hakra river valleys, may have worshiped an important mother goddess symbolizing fertility.[11] Excavations of Indus Valley Civilisation sites show seals with animals and "fire‑altars", indicating rituals associated with fire. A linga-yoni of a type similar to that which is now worshiped by Hindus has also been found.Evolution of Hinduism in India
"Priest King" of Indus Valley Civilisation
After 200 BCE, several schools of thought were formally codified in the Indian philosophy, including Samkhya, Yoga, Nyaya, Vaisheshika, Purva-Mimamsa and Vedanta.[20] Hinduism, otherwise a highly theistic religion, hosted atheistic schools and atheistic philosophies. Other Indian philosophies generally regarded as orthodox include Samkhya and Mimamsa.
Rise of Shramana Religions
Mahavira the 24th Jain Tirthankara (599–527 BCE), stressed five vows, including ahimsa (non-violence) and asteya (non-stealing). Gautama Buddha, who founded Buddhism, was born to the Shakya clan just before Magadha (which lasted from 546–324 BCE) rose to power. His family was native to the plains of Lumbini, in what is now southern Nepal. Indian Buddhism peaked during the reign of Ashoka the Great of the Mauryan Empire, who patronised Buddhism following his conversion and unified the Indian subcontinent in the 3rd century BCE. He sent missionaries abroad, allowing Buddhism to spread across Asia.[21] Indian Buddhism declined following the loss of royal patronage offered by the Kushan Empire and such kingdoms as Magadha and Kosala.The decline of Buddhism in India has been attributed to a variety of factors, which include the resurgence of an aggressive Hinduism in the 10th and 11th centuries under Sankaracharya, the later Turkish invasion, the Buddhist focus on renunciation as opposed to familial values and private property, Hinduism's own use and appropriation of Buddhist and Jain ideals of renunciation and ahimsa, etc. Although Buddhism virtually disappeared from mainstream India by the 11th century CE, its presence remained and manifested itself through other movements such as the Bhakti tradition, Vaishnavism and the Bauls of Bengal, who are influenced by the Sahajjyana form of Buddhism that was popular in Bengal during the Pala period.
Bhakti Movement
During the 14–17th centuries, when North India was under Muslim rule, the Bhakti movement swept through Central and Northern India. The Bhakti movement was initiated by a loosely associated group of teachers, or sants. Chaitanya Mahaprabhu, Vallabhacharya, Surdas, Meera Bai, Kabir, Tulsidas, Ravidas, Namdeo, Tukaram and other mystics were some of the sants in the North. They taught that people could cast aside the heavy burdens of ritual and caste, and the subtle complexities of philosophy, and simply express their overwhelming love for God. This period was also characterised by an abundance of devotional literature in vernacular prose and poetry in the ethnic languages of the various Indian states or provinces. The Bhakti movement gave rise to several different movements throughout India.During the Bhakti movement, many Hindu groups regarded as outside the traditional Hindu caste system followed Bhakti traditions by worshipping/following saints belonging to their respective communities. For example, Guru Ravidas was a Chamar of Uttar Pradesh; Guru Parsuram Ramnami was a Chura of Chhatisgarh; and Maharishi Ram Naval was a Bhangi of Rajasthan. In their lifetimes, several of these saints even went to the extent of fighting conversion from foreign missionaries, encouraging only Hinduism within their communities. In Assam for example, tribals were led by Gurudev Kalicharan Bramha of the Brahmo Samaj; in Nagaland by Kacha Naga; and in Central India by Birsa Munda, Hanuman Oaron, Jatra Bhagat and Budhu Bhagat.
Sikhism
Main article: Sikhism in India
Guru Nanak (1469–1539) was the founder of Sikhism. The Guru Granth Sahib was first compiled by the fifth Sikh guru, Guru Arjan Dev,
from the writings of the first five Sikh gurus and others saints who
preached the concept of universal brotherhood, including those of the
Hindu and Muslim faith. Before the death of Guru Gobind Singh, the Guru Granth Sahib was declared the eternal guru. Sikhism recognises all humans as equal before Waheguru,[22] regardless of color, caste or lineage.[23] Sikhism strongly rejects the beliefs of fasting (vrata), superstitions, idol worship[24][25] and circumcision.[26][27]Introduction of Monotheistic(Abrahamic) religions
Judaism
Interior of Paradesi Synagogue in Kochi, the oldest still-active synagogue in India
Main article: History of the Jews in India
Jews first arrived as traders from Judea in the city of Kochi, Kerala, in 562 BCE.[28] More Jews came as exiles from Israel in the year 70 CE, after the destruction of the Second Temple.[29]Christianity
Relationship of the St. Thomas Christian groups
Main article: Christianity in India
The works of scholars and Eastern Christian writings say that Christianity was introduced to India by Thomas the Apostle, who visited Muziris in Kerala in 52 CE and baptised Kerala's Jewish settlements, who are known as Saint Thomas Christians (also known as Syrian Christians or Nasrani) today.[30][31][32][33][34]
Although the exact origins of Christianity in India remain unclear,
there is a general scholarly consensus that Christianity was rooted in
India by the 3rd century AD, including some communities who used Syriac liturgically, and it is a possibility that the religion's existence in India extends to as far back as the 1st century.[35][36][37] Christianity in India has different denominations, like Roman Catholicism, Oriental Orthodox, and Protestantism.Most Christians reside in South India, particularly in Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Goa.[38][39] There are also large Christian populations in the North-east Indian states.[40] Christianity in India was expanded in the 16th Century by Catholic Portuguese expeditions and by Protestant British and American missionaries in the 18th century.[41]
Islam
Main article: Islam in India
Though Islam came to India in the early 7th century with the advent of Arab traders in Malabar coast, Kerala,
it started to become a major religion during the Muslim rule in the
Indian subcontinent. Islam's spread in India mostly took place under the
Delhi Sultanate (1206–1526) and the Mughal Empire (1526–1858), greatly aided by the mystic Sufi tradition.[42]As of 2011, there were about 177 Million Muslims in India, comprising 14.2% of the total population.[43]
Communalism
Communalism has played a key role in shaping the religious history of modern India. As an adverse result of the British Raj's divide and rule policy, British India was partitioned along religious lines into two states—the Muslim-majority Dominion of Pakistan (comprising what is now the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh) and the Hindu-majority Union of India (later the Republic of India). The 1947 Partition of India led to rioting amongst Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs in Punjab, Bengal, Delhi, and other parts of India; 500,000 died as a result of the violence. The twelve million refugees that moved between the newly founded nations of India and Pakistan composed one of the largest mass migrations in modern history.Δ[›][44] Since its independence, India has periodically witnessed large-scale violence sparked by underlying tensions between sections of its majority Hindu and minority Muslim communities. The Republic of India is secular; its government recognises no official religion.Demographics
See also: Hinduism in India, Islam in India, Christianity in India, History of Buddhism in India, Sikhism in India, Jainism in India, History of the Jews in India, Parsi people, Bahá'í Faith in India, Tribal religions in India and Irreligion in India
Hinduism is an ancient religion (although Hinduism is diverse, with monotheism, henotheism, polytheism, panentheism, pantheism, monism, atheism, agnosticism, and gnosticism being represented[45][46][47][48]), and Hinduism is also the largest religious grouping in India; its more than 1 billion adherents (2001) compose 80.5%[49] of the population. The term Hindu, originally a geographical description, derives from the Sanskrit, Sindhu, (the historical appellation for the Indus River), and refers to a person from the land of the river Sindhu.[citation needed]
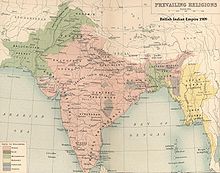
Map of the British Indian Empire in 1909, shaded by prevailing religion.
See also: Demographics of India
Prayer flags above the buddhist monastery (gompa) of Tanze, in the Kurgiakh Valley. The wind is believed to propagate prayers printed on the flags.
Jainism is a non-theistic Indian religion and philosophical system originating in Iron Age India. Jains compose 0.4% (around 4.2 million) of India's population, and are concentrated in the states of Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan.[53] Although Jainism is usually believed to be atheistic/non-theistic, Paul Dundas writes, "While Jainism is, as we have seen, atheist in the limited sense of rejection of a creator god and the possibility of the intervention of such a being in human affairs, it nonetheless must be regarded as a theist religion in the more profound sense that it accepts the existence of a divine principle, the parmatman, often in fact referred to as 'God' (e.g. ParPr 114-16), existing in potential state within all beings".[60]
Paul Dundas writes that most British judges of the 19th century "had no doubts about the independent nature and origin of Jainism".[61] In 1847, one judge wrote that religious minorities like Jains, Parsis, and Sikhs "Had nothing or next to nothing in common with brahmanical worship".[61] Another judge noted in 1874 that Jains could not be subject to Hindu law because "the term Hindoos means persons within the purview of the shastras, which shastras are at the bottom of Hindu law. If a person is out of that purview, Hindoo law cannot be applied to him"[61] He does note, "the earliest censuses of India suggest that many Jains and members of other religious groups saw themselves as in fact constituting varieties of Hinduism and, according to the Census Report for the Punjab of 1921, 'in view of the unwillingness of large number of Jains and Sikhs to be classed separately from Hindus, permission was given to record such persons as Jain-Hindus and Sikh-Hindus".[61] He does recognise the "preconceptions of the census enumerators" influenced the census. Furthermore, he adds the term "Jain-hindu" was an 'unhappy and artificial compromise".
Sikhism began in sixteenth century North India with the teachings of Guru Nanak and nine successive human gurus. As of 2001, there were 19.2 million Sikhs in India. Punjab is the spiritual home of Sikhs, and is the only state in India where Sikhs form a majority. There are also significant populations of Sikhs in neighbouring Delhi and Haryana, both of which were historically part of Punjab.
A popular Bahá'í House of Worship in Delhi, India, located at 28°33′11.46″N 77°15′35.10″E
The interior of the Paradesi Synagogue in Cochin.
Around 0.07% of the people did not state their religion in the 2001 census.
Statistics
There are six religions in India which have been awarded "National minority" status—Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Jains, Buddhists and Zoroastrians.[64][65]- Population trends for major religious groups in India (1951–2011)
| Religious group |
Population % 1951 |
Population % 1961 |
Population % 1971 |
Population % 1981 |
Population % 1991 |
Population % 2001 |
Population % 2011[1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hinduism | 84.1% | 83.45% | 82.73% | 82.30% | 81.53% | 80.46% | 79.80% |
| Islam | 9.8% | 10.69% | 11.21% | 11.75% | 12.61% | 13.43% | 14.23% |
| Christianity | 2.3% | 2.44% | 2.60% | 2.44% | 2.32% | 2.34% | 2.30% |
| Sikhism | 1.79% | 1.79% | 1.89% | 1.92% | 1.94% | 1.87% | 1.72% |
| Buddhism | 0.74% | 0.74% | 0.70% | 0.70% | 0.77% | 0.77% | 0.70% |
| Jainism | 0.46% | 0.46% | 0.48% | 0.47% | 0.40% | 0.41% | 0.37% |
| Zoroastrianism | 0.13% | 0.09% | 0.09% | 0.09% | 0.08% | 0.06% | n/a |
| Other religions / No religion | 0.43% | 0.43% | 0.41% | 0.42% | 0.44% | 0.72% | 0.9% |
- Characteristics of religious groups[1]
| Religious group |
Population (2011) % |
Growth (2001-2011)[66] |
Sex ratio (2011) (total) |
Sex ratio (2011) (rural) |
Sex ratio (2011) (urban) |
Sex ratio (2011) (child) |
Literacy (2011) (%) |
Work participation (2011) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hinduism | 79.80% | 16.8% | 939 | 946 | 921 | 925 | 65.1% | 40.4% |
| Islam | 14.23% | 24.6% | 951 | 957 | 941 | 950 | 59.1% | 31.3% |
| Christianity | 2.30% | 15.5% | 1023 | 1008 | 1046 | 964 | 80.3% | 39.7% |
| Sikhism | 1.72% | 8.4% | 903 | 905 | 898 | 786 | 69.4% | 37.7% |
| Buddhism | 0.70% | 6.1% | 965 | 960 | 973 | 942 | 72.7% | 40.6% |
| Other religions | 0.66% | n/a | 1008 | 1009 | 1006 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Jainism | 0.37% | 5.4% | 954 | 935 | 959 | 870 | 94.1% | 32.9% |
| Religion not specified | 0.24% | n/a | 959 | 947 | 975 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
Law
Main articles: Constitution of India, Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles and Fundamental Duties of India, Secularism in India and Indian religion § Status in the Republic of India
The preamble to the Constitution of India proclaims India a "sovereign socialist secular democratic republic". The word secular was inserted into the Preamble by the Forty-second Amendment Act of 1976.
It mandates equal treatment and tolerance of all religions. India does
not have an official state religion; it enshrines the right to practise,
preach, and propagate any religion. No religious instruction is
imparted in government-supported schools. In S. R. Bommai vs. Union of India, the Supreme Court of India held that secularism was an integral tenet of the Constitution.[67]Freedom of religion is a fundamental right according to the Indian Constitution. The Constitution also suggests a uniform civil code for its citizens as a Directive Principle.[68] This has not been implemented until now as Directive Principles are Constitutionally unenforceable. The Supreme Court has further held that the enactment of a uniform civil code all at once may be counter-productive to the unity of the nation, and only a gradual progressive change should be brought about (Pannalal Bansilal v State of Andhra Pradesh, 1996).[69] In Maharishi Avadesh v Union of India (1994) the Supreme Court dismissed a petition seeking a writ of mandamus against the government to introduce a common civil code, and thus laid the responsibility of its introduction on the legislature.[70]
Major religious communities not based in India continue to be governed by their own personal laws. Whilst Muslims, Christians, Zoroastrians, and Jews have personal laws exclusive to themselves; Hindus, Jains, Buddhists and Sikhs are governed by a single personal law known as Hindu personal law. Article 25 (2)(b) of the Constitution of India states that references to Hindus include "persons professing the Sikh, Jain or Buddhist religion".[71] Furthermore, the Hindu Marriage Act ,1955 defines the legal status of Jains, Buddhists and Sikhs as legal Hindus but not "Hindus by religion".[72] Supreme Court in 2005 gave verdict that Jains, Sikhs and Buddhist are part of broader Hindu fold,as they are Indic religions and interconnected to each other, though they are distinct religions.[73] The only Indian religion exclusively covered under the secular ("civil") law of India is Brahmoism starting from Act III of 1872.
Aspects
Religion plays a major role in the Indian way of life.[74] Rituals, worship, and other religious activities are very prominent in an individual's daily life; it is also a principal organiser of social life. The degree of religiosity varies amongst individuals; in recent decades, religious orthodoxy and observances have become less common in Indian society, particularly amongst young urban-dwellers.Rituals
A notable feature in religious ritual is the division between purity and pollution. Religious acts presuppose some degree of impurity, or defilement for the practitioner, which must be overcome, or neutralised, before or during ritual procedures. Purification, usually with water, is thus a typical feature of most religious action.[76] Other characteristics include a belief in the efficacy of sacrifice and concept of merit, gained through the performance of charity or good works, that will accumulate over time and reduce sufferings in the next world.[76]
Devout Muslims offer five daily prayers at specific times of the day, indicated by adhan (call to prayer) from the local mosques. Before offering prayers, they must ritually clean themselves by performing wudu, which involves washing parts of the body that are generally exposed to dirt or dust. A recent study by the Sachar Committee found that 3–4% of Muslim children study in madrasas (Islamic schools).[77]
Diet
See also: Vegetarianism and religion and Fasting
Dietary habits are significantly influenced by religion. Almost one-third of Indians practice lacto-vegetarianism. Vegetarianism is less common amongst Sikhs and almost uncommon amongst Muslims, Christians, Bahá'ís, Parsis and Jews.[78]
Jainism requires monks and laity, from all its sects and traditions, to
be vegetarian. Furthermore, the religion also bars jains from eating
any vegetable that involves digging it from the ground. This rule,
therefore, excludes potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots, garlic, peanuts,
raddish etc. from Jain diet. Islam and Judaism bar pork.Ceremonies
A Hindu marriage.
Muslims practise a series of life-cycle rituals that differ from those of Hindus, Jains, and Buddhists.[81] Several rituals mark the first days of life—including whispering call to prayer, first bath, and shaving of the head. Religious instruction begins early. Male circumcision usually takes place after birth; in some families, it may be delayed until after the onset of puberty.[81]
Marriage requires a payment by the husband to the wife and the solemnization of a marital contract in a social gathering.[81] On the third day after burial of the dead, friends and relatives gather to console the bereaved, read and recite the Quran, and pray for the soul of the deceased.[81] Indian Islam is distinguished by the emphasis it places on shrines commemorating great Sufi saints.[81]
Pilgrimages
The largest religious gathering ever held on Earth, the 2001 Maha Kumbh Mela held in Prayag attracted around 70 million Hindus from around India.
The Sanchi Stupa in Madhya Pradesh is the oldest stone structure in India. Built by Emperor Asoka in the 3rd century BCE, it houses the relics of Buddha Siddhartha Gautama.
Rumtek Monastery in Sikkim is one of the major tourist attractions of North-East India.
Maramon Convention, the largest annual Christian gathering in Asia, organised by the Mar Thoma Church.
The Himalayan towns of Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri compose the Char Dham (four abodes) pilgrimage circuit. The Kumbh Mela (the "pitcher festival") is one of the holiest of Hindu pilgrimages that is held every four years; the location is rotated amongst Allahabad, Haridwar, Nashik, and Ujjain. The Thalaimaippathi at Swamithope is the leading pilgrim center for the Ayyavazhis.
Amongst the Eight Great Places of Buddhism, seven are in India. Bodh Gaya, Sarnath and Kushinagar are the places where important events in the life of Gautama Buddha took place. Sanchi hosts a Buddhist stupa erected by the emperor Ashoka. Many Buddhist monasteries dot the Himalayan foothills of India, where Buddhism remains a major presence. These include the Rumtek Monastery, Enchey Monastery and Pemayangtse Monastery in Sikkim, the Tawang Monastery in Arunachal Pradesh, the Kye Monastery and Tabo Monastery in Spiti, the Ghum Monastery in Darjeeling, and Durpin Dara Monastery in Kalimpong, the Thikse Monastery in Leh, the Namgyal Monastery in Dharamshala, among many others.
For Muslims, the Dargah Shareef of Khwaza Moinuddin Chishti in Ajmer is a major pilgrimage site. Other Islamic pilgrimages include those to the Tomb of Sheikh Salim Chishti in Fatehpur Sikri, Jama Masjid in Delhi, and to Haji Ali Dargah in Mumbai. Dilwara Temples in Mount Abu, Palitana, Pavapuri, Girnar and Shravanabelagola are notable pilgrimage sites (tirtha) in Jainism.
The Harmandir Sahib in Amritsar is the most sacred gurdwara of Sikhism, while the Lotus Temple in Delhi is a prominent house of worship of the Bahá'í faith.
Relatively new pilgrimage sites include the samadhi of Meher Baba in Meherabad, which is visited by his followers from around the world [85] and the Saibaba temple in Shirdi. [86]
Minority Beliefs and Sects
Hinduism contains many different sub-cultures just like most other religions. The major aspects outlined above hold true for the majority of the Hindu population, but not all. Just as each state is home to an individual language, Hinduism harbors various sub-cultures whose traditions may or may not be shared by other Indians. A sect from Gujarat called the Prajapatis for example, hold water as the sacred ornament to every meal. Before and after a meal, an individual is expected to pour water in the palms of their right hand and sip the water three times.[87] This is often seen as a purification gesture: food is regarded as being holy and every individual must purify themselves before touching their food.Other minor sects in India carry no specific name, but they are uniquely identified by the last names of each family. This convention is used more frequently in South India than North India. For example, a relatively prominent sect in southern India prohibits making important decisions, commencing new tasks, and doing other intellectually or spiritually engaged actions after sunset. Historians believe that this tradition was derived from the concept of Rahukaalam, in which Hindus believe that a specific time period of the day is inauspicious. Stringent family beliefs are thought to have led to the development of a more constrained religious hierarchy.[88] Over time, this belief was extended to discourage taking major actions and even staying awake for long periods of time after sunset. Examples of families which follow this tradition include Gudivada, Padalapalli, Pantham, and Kashyap.[87]
Religion and politics
Main articles: Indian Mujahideen, Jamaat-e-Islami Hind and List of organizations banned by the Government of India
See also: Status of religious freedom in India
Takht Sri Hazur Sahib, Nanded, built over the place where Guru Gobind Singh was cremated in 1708, the inner chamber is still called Angitha Sahib.
Politics
Religious ideology, particularly that expressed by the Hindutva movement, has strongly influenced Indian politics in the last quarter of the 20th century. Many of the elements underlying India's casteism and communalism originated during the rule of the British Raj, particularly after the late 19th century; the authorities and others often politicised religion.[89] The Indian Councils Act 1909 (widely known as the Morley-Minto Reforms Act), which established separate Hindu and Muslim electorates for the Imperial Legislature and provincial councils, was particularly divisive. It was blamed for increasing tensions between the two communities.[90]Due to the high degree of oppression faced by the lower castes, the Constitution of India included provisions for affirmative action for certain sections of Indian society. Many states ruled by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) introduced laws that made conversion more difficult; they assert that such conversions are often forced or allured.[91] The BJP, a national political party, also gained widespread media attention after its leaders associated themselves with the Ram Janmabhoomi movement and other prominent religious issues.[92]
A well known accusation that Indian political parties make for their rivals is that they play vote bank politics, meaning give political support to issues for the sole purpose of gaining the votes of members of a particular community. Both the Congress Party and the BJP have been accused of exploiting the people by indulging in vote bank politics. The Shah Bano case, a divorce lawsuit, generated much controversy when the Congress was accused of appeasing the Muslim orthodoxy by bringing in a parliamentary amendment to negate the Supreme Court's decision. After the 2002 Gujarat violence, there were allegations of political parties indulging in vote bank politics.[93]
During an election campaign in Uttar Pradesh, the BJP released an inflammatory CD targeting Muslims.[94] This was condemned by the Communist Party of India (Marxist) as playing the worst kind of vote bank politics.[95] Caste-based politics is also important in India; caste-based discrimination and the reservation system continue to be major issues that are hotly debated.[96][97]
Education
Several political parties have been accused of using their political power to manipulate educational content in a revisionist manner. During the Janata Party government (1977–1979), the government was accused of being too sympathetic to the Muslim viewpoint. In 2002, the BJP-led NDA government tried to change the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) school textbooks through a new National Curriculum Framework.[98]Some media referred to it as the "saffronisation" of textbooks, saffron being the color of BJP flag.[98] The next government, formed by the UPA and led by the Congress Party, pledged to de-saffronise textbooks.[99] Hindu groups alleged that the UPA promoted Marxist and pro-Muslim biases in school curricula.[100][101]
India is the home and birthplace of four major religions: Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism," and also the home to Judaism and Christianity.[102] All of these religions were passed down over time, not with the help of immigrants. Most people see India as being strongly based upon Hinduism, however Hinduism cannot be characterized as a religion. Millions of people in India have been taught through heritages, that Hinduism is a philosophy. "Hindu" for many Persians and Arabs was not considered a religious word but as a geographical and cultural one, used to describe the land next to the Indus River.[103]
Conflicts
Main articles: Religious violence in India and Terrorism in India
See also: Religious conflicts in India
Aftermath of Hindu-Muslim clashes in Calcutta following the 1946 Direct Action Day.
Alongside other major Indian independence leaders, Mahatma Gandhi and his shanti sainiks ("peace soldiers") worked to quell early outbreaks of religious conflict in Bengal, including riots in Calcutta (now in West Bengal) and Noakhali District (in modern-day Bangladesh) that accompanied Muhammad Ali Jinnah's Direct Action Day, which was launched on 16 August 1946. These conflicts, waged largely with rocks and knives and accompanied by widespread looting and arson, were crude affairs. Explosives and firearms, which are rarely found in India, were far less likely to be used.[104]
Many of Ahmedabad's buildings were set on fire during the 2002 Gujarat violence.
This triggered Indira Gandhi's assassination by her outraged Sikh bodyguards on 31 October 1984, which set off a four-day period during which Sikhs were massacred; The Government of India reported 2,700 Sikh deaths however human rights organisations and newspapers report the death toll to be 10,000–17,000. In the aftermath of the riot, the Government of India reported 20,000 had fled the city, however the PUCL reported "at least" 50,000 displaced persons.[106]
The most affected regions were neighbourhoods in Delhi. Human rights organisations and the newspapers believe the massacre was organised.[107] The collusion of political officials in the massacres and the failure to prosecute any killers alienated normal Sikhs and increased support for the Khalistan movement. The Akal Takht, the governing religious body of Sikhism, most definitely considers the killings to be a genocide.[108]
Other incidents include the 1992 Bombay Riots that followed the demolition of the Babri Mosque as a result of the Ayodhya debate, and the 2002 Gujarat violence that followed the Godhra Train Burning—in the latter, more than 2,000 Muslims were killed.[109] Terrorist activities such as the 2005 Ram Janmabhoomi attack in Ayodhya, the 2006 Varanasi bombings, the 2006 Jama Masjid explosions, and the 11 July 2006 Mumbai Train Bombings are often blamed on communalism. Lesser incidents plague many towns and villages; representative was the killing of five people in Mau, Uttar Pradesh during Hindu-Muslim rioting, which was triggered by the proposed celebration of a Hindu festival.[109]
| Year | Riot | State / Region | Cause | Aftermath |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Anti Sikh riots | Delhi | Assassination of Indira Gandhi by her Sikh Bodyguards after Operation Blue Star of the Golden Temple in Amritsar | Government of India reported 2,700 Sikh deaths and 20,000 displaced. PUCL and newspapers report death toll to be 10,000–17,000 and "at least" 50,000 displaced.[106] |
|
|
Bombay Riots | Mumbai | Demolition of Babri Mosque by Hindus as considered as Ram Janmbhoomi by artifacts | 900 people dead |
|
|
Gujarat Riots | Gujarat | Godhra train burning by Muslim mob | Per the Government of Gujarat, 1,044 people were killed – 790 Muslims and 254 Hindus.[110] Most independent groups report 200 – 500 killed in these riots,.[111] Police records list 29 dargahs, 20 mosques, 17 temples and three churches as damaged in the months of March and April.[112] |
|
|
Kandhamal riots | Odisha | Murder of Swami Lakshmanananda | Over 20 killed and over 12,000 displaced |
|
|
2012 Assam violence | Assam | Murder of four former Bodo Liberation Tigers men in Kokrajhar by Bengali Muslim settlers[citation needed] | 77 killed and over 17,000 displaced (as of 8 August 2012) |
|
|
2013 Muzaffarnagar riots | Uttar Pradesh | Harassment of Hindu girl and murder of her brothers by Muslim mob in Kawal village of Muzaffarnagar[113] | 47 killed[114] and over 10,000 displaced[115] (as of 14 September 2013) |

























No comments:
Post a Comment